WHAT IS INSIDE THIS PACKAGE?
- OpenVPN authentication server and client (openvpn_authd.pl)
- OpenVPN server add-on for dynamically configuring clients from LDAP directory
COMPONENTS
OpenVPN authentication server
VPN userland daemon. Currently you can authenticate your openvpn client using the following authentication backends:
- LDAP
- Kerberos5
- any SQL database supported by perl DBI driver
- IMAPv4 server
- POP3 server
- plain file containing passwords
- SASL library
- PAM library
- Radius service
- custom certificate validation algorithm.
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
- perl (authentication server is written in perl)
- c compiler (for compiling authentication client)
system package manager or by running the following command:
perl -MCPAN -e 'install ' - Log::Log4perl – for highly configurable logging
- Log::Dispatch – Log4perl drivers
- Net::Server – for simple and reliable network server infrastructure
- Net::LDAP – for ldap backend
- IO::Socket::SSL – for providing secure transport for LDAP, IMAP and POP3 backends
- DBI and corresponding DBI module – for DBI/SQL backend
- Authen::Krb5::Simple – for Kerberos5 backend
- Authen::SASL – for sasl bind support in LDAP backend
- Authen::SASL::Cyrus – for SASL backend
- Authen::PAM – for PAM backend
- Authen::Radius – for Radius backend
when using ‘pass_attr’ authentication method.
- Crypt::PasswdMD5 – for validating md5 hashed crypt(3) passwords
- Digest::MD5 – for validating md5 string hashes
- Digest::SHA1 – for validation of sha1 string hashes
- Crypt::SmbHash – for validation of ntlm hashes
- Digest::Tiger – for validation of Tiger string hashes
- Digest::Whirlpool – for validation of Whirlpool string hashes
INSTALLATION
- Install, configure & test openvpn daemon (i guess you already did that)
- Unpack openvpn_authd (i guess you already did that too)
- Compile openvpn_authc
cd "c" && make- Create default configuration file
./bin/openvpn_authd.pl --default-conf > ./etc/openvpn_authd.conf- List supported authentication backends
./bin/openvpn_authd.pl --list- Read authentication backend documentation
./bin/openvpn_authd.pl --doc - Adjust configuration your file
vi ./etc/openvpn_authd.conf- Start server in non daemon and debug mode
./openvpn_authd.pl —no-daemon —debug
- Create file with username and password
echo "joe" > /tmp/sample_auth.txt
echo "joes_password" >> /tmp/sample_auth.txt- Create & adjust openvpn_authc configuration file
./bin/openvpn_authc --default-config > /etc/openvpn_authc.conf
vi /etc/openvpn_authc.conf- Check if everything works…
export common_name="someuser.example.org"
export untrusted_ip="1.2.3.4"
export untrusted_port="3456"
export script_type="auth-user-pass-verify"
./bin/openvpn_authc -v /tmp/sample_auth.txt- Doesn’t work? Check your syslog, there’s alot of debug output…
- Works? Hooray, configure your openvpn daemon to use openvpn_authc:
# /etc/openvpn/openvpn-server.conf
# use external additional authentication
# using openvpn_authd
auth-user-pass-verify /path/to/openvpn_authd/bin/openvpn_authc via-fileChroot install
openvpn_authd, but the best way is to chroot both of them (openvpn_authd was designed to run in chroot from scratch)
- Create openvpn chroot directory (see OPENVPN_CHROOT_STRUCTURE.TXT)
- Create openvpn_authd chroot structure (see OPENVPN_AUTHD_CHROOT_STRUCTURE.TXT)
- Configure your syslogd (or even better, syslog-ng) to put listening sockets in BOTH chroots
- Restart syslogd :)
- Compile openvpn_authc statically
cd c && make static- Reconfigure your openvpn to chroot (see samples/openvpn-server-chroot.conf)
- Reconfigure openvpn_authd to put listening socket to openvpn chroot
(you don’t need to do this if openvpn_authd is listening at tcp address)
- Edit /etc/openvpn_authc.conf and set directive hostname
- Put statically compiled openvpn_authc binary into /bin
- Put /bin/sh file into /bin and /bin/sh linked libraries into /lib(64)
# ldd ../bin/sh
libtermcap.so.2 => /lib64/libtermcap.so.2 (0x00002b636bf5c000)
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00002b636c05f000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00002b636c163000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00002b636be3c000)- Restart openvpn and openvpn_authd && test configuration
OpenVPN client configuration
—client-connect script or can be used for periodic generation of client configuration files.
HOWTO
- Create default configuraton file.
./openvpnClientConnectLDAP --default-config- Change configuration to suit your needs
- Run it on regular basis to create client configuration file OR set client-connect /path/to/openvpnClientConnectLDAP.pl to your openvpn server configuration file.
搭建基于Mysql认证的Openvpn服务器
维基百科上对Openvpn的说明:
OpenVPN允许参与建立VPN的单点使用公开密钥、電子證書、或者用户名/密碼来进行身份验证。它大量使用了OpenSSL加密库中的SSLv3/TLSv1协议函数库。目前OpenVPN能在Solaris、Linux、OpenBSD、FreeBSD、NetBSD、Mac OS X与Windows 2000/XP/Vista上运行,並包含了许多安全性的功能。它并不是一个基于Web的VPN软件,也不与IPsec及其他VPN软件包兼容。
OpenVPN使用OpenSSL库加密数据与控制信息:它使用了OpenSSL的加密以及验证功能,意味着,它能够使用任何OpenSSL支持的算法。它提供了可选的数据包HMAC功能以提高连接的安全性。此外,OpenSSL的硬件加速也能提高它的性能。OpenVPN提供了多种身份验证方式,用以确认参与连接双方的身份,包括:预享私钥,第三方证书以及用户名/密碼组合。预享密钥最为简单,但同时它只能用于建立点对点的VPN;基于PKI的第三方证书提供了最完善的功能,但是需要额外的精力去维护一个PKI证书体系。OpenVPN2.0后引入了用户名/口令组合的身份验证方式,它可以省略客户端证书,但是仍有一份服务器证书需要被用作加密。
今天准备搭建一个Openvpn服务器,基于mysql验证,验证方式为用户名密码+证书,并提供流量控制。Openvpn是目前我所用过的vpn里面稳定性最好的,特别是在今天国内日益严峻的网络形式下,Openvpn绝对是一种不可多得的翻墙利器,当然,前提你必须有一台国外的服务器或者VPS。它可以基于tcp协议,同时也可以基于udp协议,端口可以随意设置,随时更改,加密性好。
配置开始,本篇以debian6.0系统为例,ubuntu通用。
首先安装openvpn、mysql-server以及pam-mysql模块。
```apt-get install openvpn mysql-server libpam-mysql sasl2-bin```
Openvpn配置:
复制生成证书的脚本
```cp -R /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/easy-rsa/ /etc/openvpn/```
修改证书变量
```cd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/2.0/
nano vars```
修改最后几行,修改成你自定义的信息,不修改也可以。
```export KEY_COUNTRY="HK"
export KEY_PROVINCE="HK"
export KEY_CITY="Hongkong"
export KEY_ORG="FUCKCNNet"
export KEY_EMAIL="webmaster@your.domain"```
保存退出,然后开始清理。
```source ./vars
./clean-all```
接着开始生成证书。
```./build-ca
./build-key-server server
./build-key client1
./build-dh```
全部按默认回车,有提示下面两个问题的,输入y回车即可。
Sign the certificate?
1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit?
开始建立数据库。
登录mysql:
```mysql -uroot -p```
新建一个数据库:
mysql>
```CREATE DATABASE openvpn;```
切换数据库:
```USE openvpn;```
创建一个mysql用户专门用于管理Openvpn的数据库:
```GRANT ALL ON openvpn.* TO 'openvpn'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';```
用户名为openvpn,密码为password,可按自己的需要修改替换。
建立用户数据表:
```CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `user` (
`username` char(32) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`password` char(128) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`active` int(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1',
`creation` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`name` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`email` char(128) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`note` text COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci,
`quota_cycle` int(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT '30',
`quota_bytes` bigint(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '10737418240',
`enabled` int(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1',
PRIMARY KEY (`username`),
KEY `idx_active` (`active`),
KEY `idx_enabled` (`enabled`)
) DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci;```
创建日志数据表:
```CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `log` (
`username` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`start_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`end_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00',
`trusted_ip` varchar(64) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`trusted_port` int(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`protocol` varchar(16) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`remote_ip` varchar(64) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`remote_netmask` varchar(64) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`bytes_received` bigint(20) DEFAULT '0',
`bytes_sent` bigint(20) DEFAULT '0',
`status` int(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1',
KEY `idx_username` (`username`),
KEY `idx_start_time` (`start_time`),
KEY `idx_end_time` (`end_time`)
) DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci;```
数据库的操作就完成了,退出数据库。
```exit```
下面开始修改openvpn让它支持mysql的验证。
```nano /etc/pam.d/openvpn```
输入以下内容:
```auth sufficient pam_mysql.so user=openvpn passwd=password host=localhost db=openvpn table=user usercolumn=username passwdcolumn=password where=active=1 sqllog=0 crypt=1
account required pam_mysql.so user=openvpn passwd=password host=localhost db=openvpn table=user usercolumn=username passwdcolumn=password where=active=1 sqllog=0 crypt=1```
上面的用户名密码替换成你前面设置的mysql用户名密码。
其中数据库、用户名、密码按照自己的实际情况设置。
crypt 表示密码在数据库中加密存储的方式,含义如下:
0 (or “plain”):不加密,明文存储。不推荐使用。
1 (or “Y”):使用crypt(3)函数,相当于MySQL 中的ENCRYPT()函数。
2 (or “mysql”):使用MySQL 的PASSWORD()函数。PAM 可能与MySQL 的函数不同,不推荐使用。
3 (or “md5″):使用MD5。
4 (or “sha1″):使用SHA1。
上面的例子使用的是1。
编辑/etc/default/saslauthd
```nano /etc/default/saslauthd```
把START=no改成START=yes。
重新启动saslauthd。
```/etc/init.d/saslauthd restart```
先测试一下配置是否正确,先添加在mysql里面添加一个test用户,密码也是test。
```mysql -uopenvpn -p```
mysql>
```USE openvpn;
INSERT INTO user(username, password) VALUES('test', ENCRYPT('test'));
exit```
退出以后,运行
```testsaslauthd -u test -p test -s openvpn```
如果提示
0: OK "Success."
那就说明验证通过了,如果验证没通过的话,检查一下/var/log/auth.log,看看是什么原因导致的错误。
复制Openvpn的pam验证模块到Openvpn目录:
```cp /usr/lib/openvpn/openvpn-auth-pam.so /etc/openvpn/```
复制一些刚才建立的证书到Openvpn目录。
```cp /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/2.0/keys/ca.crt /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/2.0/keys/dh1024.pem /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/2.0/keys/server.crt /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/2.0/keys/server.key /etc/openvpn/```
开始建立Openvpn的配置文件,OpenVPN 服务启动时,会扫描/etc/openvpn 目录中的.conf 文件,对于每个文件,启动一个daemon。本系统要实现UDP、TCP 登录的同时支持,可以写两份配置文件,如tcp.conf,udp.conf,即启动两个daemon,分别负责TCP和UDP协议。我一般只用UDP,所以只建立了一个server.conf。以下以udp为例。
```nano /etc/openvpn/server.conf```
参考配置文件:
```port 1194
proto udp
dev tun
ca ca.crt
cert server.crt
key server.key # This file should be kept secret
dh dh1024.pem
user nobody
group nogroup
server 172.16.8.0 255.255.255.0
ifconfig-pool-persist ipp.txt
push "redirect-gateway def1"
push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.222.222"
push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.220.220"
;push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.8.8"
;push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.4.4"
# user/password auth from mysql
plugin /etc/openvpn/openvpn-auth-pam.so openvpn
username-as-common-name
;client-to-client
keepalive 20 120
comp-lzo
max-clients 30
persist-key
persist-tun
status openvpn-status.log
log-append /var/log/openvpn/openvpn.log
verb 3
mute 5
# record in database
script-security 2
client-connect ./connect.sh
client-disconnect ./disconnect.sh```
其中,# user/password auth from mysql 下面的几行是该认证设置的关键所在。如果希望vpn用户之间可以互访,去掉;client-to-client前面的;即可。
配置文件最后两行是用来做流量控制的,下面会讲到。
同理,如果想支持TCP,建立一个tcp.conf 文件,内容跟上面相同,仅仅把下面几行修改一下即可。
```proto udp
server 172.16.8.0 255.255.255.0
status openvpn-status.log
log-append /var/log/openvpn/openvpn.log```
改为
```proto tcp
server 10.88.0.0 255.255.255.0
status openvpn-tcp.log
log-append /var/log/openvpn/tcp.log```
先为 日志文件创建目录。
```mkdir /var/log/openvpn```
新建一个/etc/openvpn/connect.sh文件。
```nano /etc/openvpn/connect.sh```
输入以下内容:
```#!/bin/bash
DB='openvpn'
DBADMIN='openvpn'
DBPASSWD='password'
mysql -u$DBADMIN -p$DBPASSWD -e "INSERT INTO log(username,start_time,trusted_ip,trusted_port,protocol,remote_ip,remote_netmask,status) VALUES('$common_name',now(),'$trusted_ip',$trusted_port,'$proto_1','$ifconfig_pool_remote_ip','$route_netmask_1',1)" $DB```
新建/etc/openvpn/disconnect.sh文件。
```nano /etc/openvpn/disconnect.sh```
输入以下内容:
```#!/bin/bash
DB='openvpn'
DBADMIN='openvpn'
DBPASSWD='password'
mysql -u$DBADMIN -p$DBPASSWD -e "UPDATE log SET end_time=now(),bytes_received=$bytes_received,bytes_sent=$bytes_sent,status=0 WHERE trusted_ip='$trusted_ip' AND trusted_port=$trusted_port AND remote_ip='$ifconfig_pool_remote_ip' AND username='$common_name' AND status=1" $DB
mysql -u$DBADMIN -p$DBPASSWD -e "UPDATE user SET active=0 WHERE user.username IN (SELECT username FROM (SELECT log.username AS username, quota_bytes FROM user, log WHERE log.username='$common_name' AND log.username=user.username AND log.status=0 AND TO_DAYS(NOW())-TO_DAYS(start_time)< =quota_cycle GROUP BY log.username HAVING SUM(bytes_received)+SUM(bytes_sent)>=quota_bytes) AS u);" $DB```
上面的数据库用户名密码替换成你设置的数据库用户名密码。
赋予文件可执行的权限。
```chmod +x /etc/openvpn/connect.sh
chmod +x /etc/openvpn/disconnect.sh```
其主要作用是:在用户连接时,在数据库log 表中新建一条记录,记录用户的IP 地址、端口号、连接时间等信息。在用户断开连接时,更新刚才添加的记录,记下用户的断开连接时间、发送数据量、接收数据量等。然后,对用户的流量进行判断,若超过配额,则将用户锁定(active=0)。
user 表中的quota_cycle 是用户的流量计算周期,quota_bytes 是用户每个周期内最多允许的流量。connect.sh 和disconnect.sh 脚本文件中调用了OpenVPN 的环境变量。OpenVPN 在执行脚本时,自动各种设置了环境变量,供脚本使用。
使用cron 每天对用户进行检查
以上操作在用户超过流量时自动将用户锁定。每天还应该执行一次检查,把已经恢复流量的用户解锁。可以通过cron实现此功能。
建立文件/etc/cron.daily/openvpn
```nano /etc/cron.daily/openvpn```
内容如下:
```#!/bin/bash
DB='openvpn'
DBADMIN='openvpn'
DBPASSWD='password'
mysql -u$DBADMIN -p$DBPASSWD -e "UPDATE user SET active=1" $DB
mysql -u$DBADMIN -p$DBPASSWD -e "UPDATE user SET active=0 WHERE
user.username IN (SELECT username FROM (SELECT log.username AS username,
quota_bytes FROM user, log WHERE log.username=user.username AND
log.status=0 AND TO_DAYS(NOW())-TO_DAYS(start_time)< =quota_cycle
GROUP BY log.username HAVING
SUM(bytes_received)+SUM(bytes_sent)>=quota_bytes) AS u);" $DB
mysql -u$DBADMIN -p$DBPASSWD -e "UPDATE user SET active=0 WHERE enabled=0" $DB```
同样把上面的数据库用户名密码替换成你设置的数据库用户名密码。
其思路是:先默认将所有用户解锁,然后将超过流量的用户锁定。同时,管理员可以通过user 表中的enabled 字段手工禁用用户。
赋予文件可执行权限:
```chmod +x /etc/cron.daily/openvpn```
修改saslauthd 的缓存时间。
saslauthd 默认有一段较长的缓存时间,在用户通过认证后的一段时间里,可以再次通过认证而不需要重新查询数据库。这样不利于实现对超流量用户的立即锁定。saslauthd 启动时有一个-t 参数,可以设置其超时时间。
修改/etc/default/saslauthd文件
```nano /etc/default/saslauthd```
saslauthd 启动时有一个-t 参数,可以设置其超时时间,最后一行的OPTIONS,添加-t 60。
```OPTIONS="-c -m /var/run/saslauthd -t 60"```
最后做一下NAT转发,否则vpn连上了也上不了网。
```iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 172.16.8.0/16 -j SNAT --to-source 服务器IP```
保存iptables规则。
```iptables-save > /etc/iptables.rules```
修改/etc/sysctl.conf
```nano /etc/sysctl.conf```
找到以下几条,去掉前面的#号即可。
```net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0```
执行以下sysctl让它马上生效。
```sysctl -p```
这样已经就可以用了,但是iptables在重启以后会失效,再完成下面这一步就OK了。
新建/etc/network/if-up.d/iptables
```nano /etc/network/if-up.d/iptables```
内容如下:
```#!/bin/sh
iptables-restore < /etc/iptables.rules```
赋予文件可执行权限
```chmod +x /etc/network/if-up.d/iptables```
重启saslauthd和openvpn。
```/etc/init.d/saslauthd restart
/etc/init.d/openvpn restart```
到这里服务器端的配置已全部完成,一个基于Mysql验证同时拥有流量控制的Openvpn服务器就诞生了。
客户端的配置,首先安装openvpn。
Openvpn官网: http://openvpn.net/
下载页面: http://openvpn.net/index.php/open-source/downloads.html
Windows用户直接下载Windows Installer即可,安装按默认安装就可以了。
接下来在服务器上拷贝三个证书文件下来,分别是ca.crt,client1.key,client1.crt,放到C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\config\目录下,新建一个myvpn.ovpn文件,用记事本打开,输入以下内容:
```client
dev tun
proto udp
remote 服务器ip 1194
resolv-retry infinite
nobind
persist-key
persist-tun
ca ca.crt
cert client1.crt
key client1.key
auth-user-pass
push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.222.222"
push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.220.220"
ns-cert-type server
redirect-gateway
keepalive 20 60
comp-lzo
verb 3
mute 20
route-method exe
route-delay 2```
保存退出后,启动Openvpn即可连接。至此,所有配置均已完成,开始呼吸自由的网络空气吧。^_^
本文大部分资料来源某网络博客.
----------------------------------------
Improving OpenVPN performance and throughput
OpenVPN, WireGuard, L2TP/IPSec, SSTP, IKEv2, PPTP, or others. If you had the luxury of choosing, which VPN protocols would you use? Therein lies my problem. In my current use case, I must find a way to improve OpenVPN performance and throughput.
You may have been following my Linux home lab build. One of the most important decisions when building your home lab is selecting the proper router/firewall for your network. After many hours of research, online comparisons, reading reviews, and watching YouTube videos, I went with the Edgerouter 10x (ER-10x). Note: this article includes my affiliate links; however, I only link to hardware and services I’ve paid for and tested myself.
Last week, I figured out that it does not support WireGuard, at least not officially, as I recently discovered (my next to-do). This isn’t a knock on the ER-10x; it’s a remarkably capable router with many business-class features, and most important, rock-solid stability. 2024 Update: I’ve replaced the ER 10x with a Peplink Balance 20x – also does not support WireGuard.
That said, my VPN service provider of choice is ovpn.com. They have many locations, excellent performance, and offer dedicated IPs with open ports at $3/month. On routers, they support WireGuard or OpenVPN.
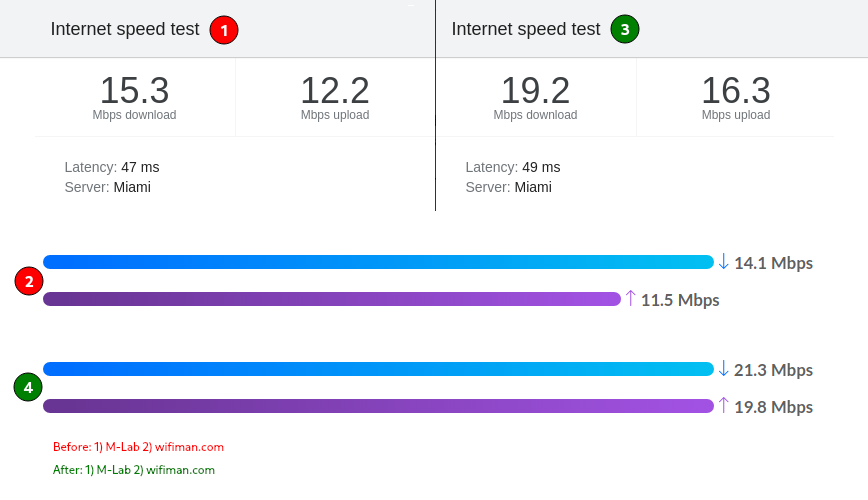
OpenVPN 2.4 internet speed test results using Google+M-Lab and wifiman.com.
The Edgerouter 10x is built on Debian Linux. This makes it a pleasure to work with because a lot of the functionality feels familiar. Over the past year, I’ve spent more time in the command line and less time using the GUI.
Setting up OpenVPN is one of those command-line-only features. However, after downloading the .ovpn file and setting it up on the router, I soon hit a crippling OpenVPN limitation. The CPU! The ER-10x features 880 MHz CPU cores, which is often overkill. However, in this case, OpenVPN performance is not very efficient as throughput largely depends on the CPU’s core speed.
On my first speed test, download speeds were around 15 Mbps download and 12 Mbps upload. I needed a solid 20 Mbps down for the IoT devices connected to a VLAN that uses that VPN connection.
My basic setup at home currently is: dual WAN with backup 4G LTE ISP auto-failover, VLANs for isolated Guest WiFI network, and IoT devices, both wired and wireless. For now, I’ll run with what I have; it works!
Improving OpenVPN Performance
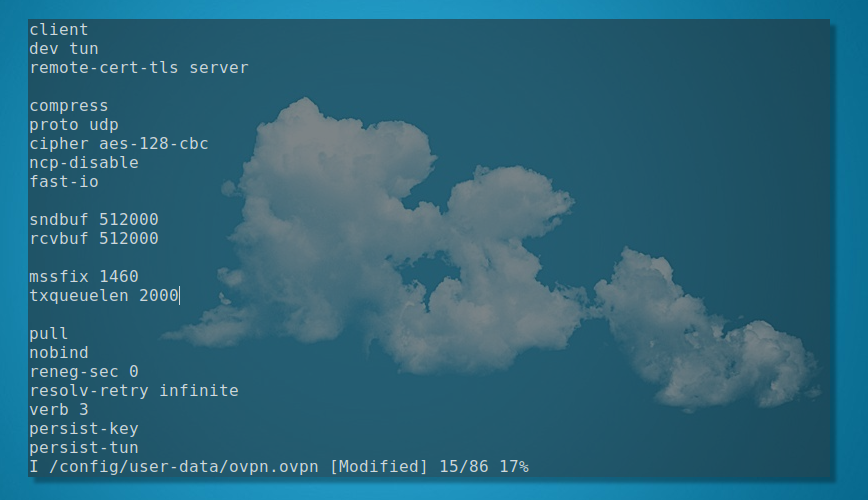
OpenVPN config Screenshot from my Manjaro i3 SSH session with the router.
Note: I’ve already verified results when I initially set up everything a week ago using my Ubuntu server over higher LAN throughput with iperf. As the hardware/CPU limits are so low on the Edgerouter, the ISP tests were very much representative of those tests. If you are using OpenVPN in a hardware-restricted setup, try the following config tweaks. I’ll try to take the time and revisit this article with some redone iperf test results. If you have the time, you can share your test results in the comments section below or by email using the “contact” link.
My ISP download speed is just over 100 Mbps. In this part of the world, this is as good as it gets for under $200 per month. That said, even before this OpenVPN setup, the IoT devices on my home network were restricted to a maximum download of 20 Mbps. I am using an EdgeSwitch to limit wired connections’ bandwidth and the Unifi controller via Unifi APs to limit wireless bandwidth. These network restrictions ensure that one or more devices don’t gobble bandwidth.
My plan? Improve OpenVPN performance as much as possible to at least hit 20 Mbps download speeds, as you can see from the above before vs. after internet speed tests. (I’ve since disabled bandwidth restrictions on the OpenVPN VLAN).
After optimizing OpenVPN’s performance, the max up/down speed is just about what the previous limits were. Let’s look at how you can go from 15 Mbps to 20 Mbps internet download speed on an 880 MHz CPU core router.
OpenVPN server Location
Whether you are using NordVPN (awesome 24/7 customer support), OVPN (best dedicated IP VPN, in my opinion), or another VPN service, the first step should be selecting the VPN servers closest to you. In my case, its servers are located in South Miami. Not much to elaborate on here… Closer is generally faster. Still, you should test locations for yourself because not all servers perform equally. Some are under more load than others. Thankfully, OVPN shows load levels for VPN server locations.
Disable compression
If the CPU isn’t a bottleneck, then feel free to enable compression. On the Edgerouter, compression will use CPU resources, leading to higher CPU usage. You can disable it with:
comp-lzo no ;deprecated - remove or use 'compress' without an algorithm
or recommended for OpenVPN version 2.4+:
compress
Providing just compress without an algorithm is the equivalent of comp-lzo no which disables compression but enables the packet framing for compression.
Use UDP for better OpenVPN performance.
With OpenVPN, in most cases, UDP is faster than TCP. TCP packets are heavier, adding overhead. TCP also numbers packets in a sequence, while UDP doesn’t. UDP uses very minimal headers, making it less resource-intensive. Here’s the config line:
proto udp
Choosing the right Cipher
By default, OpenVPN uses Blowfish,
a 128-bit cipher. Regarding the level of security you require, you will
have to decide between better encryption vs. faster throughput with
respect to CPU load. Again, especially with this 880 MHz CPU. If there’s
no CPU bottleneck, I would recommend using AES-256-GCM. In my case, I’m using AES-128-CBC as it resulted in faster OpenVPN throughput.
cipher AES-128-CBC
Disable cipher negotiation
You can set ncp-disable (disable “negotiable crypto parameters”). This completely disables cipher negotiation and instead uses what’s specified by the cipher option discussed previously. As of OpenVPN 2.4, this is now deprecated. Also, read OpenVPN Cipher Negotiation (Quick reference).
ncp-disable
Optimize TUN/TAP/UDP I/O writes
Set fast-io to optimize TUN/TAP/UDP I/O writes by avoiding a call to poll/epoll/select before the write operation.
“The purpose of such a call would normally be to block until the
device or socket is ready to accept the write. Such blocking is
unnecessary on some platforms, which don’t support write blocking on UDP
sockets or TUN/TAP devices. In such cases, one can optimize the event
loop by avoiding the poll/epoll/select call, improving CPU efficiency by 5% to 10%. This option can only be used on non-Windows systems, when proto udp is specified, and when shaper is NOT specified.” – Source.
Set send/receive buffers
You can set the UDP socket send and receive buffer sizes. On OpenVPN 2.3.9+, this defaults to the operating system’s default (usually 64K).
Add to client config (bytes):
sndbuf 512000 rcvbuf 512000
Or, if you have access, set buffers in the server config:
sndbuf 512000 rcvbuf 512000 push "sndbuf 512000" push "rcvbuf 512000"
Read more about fine-tuning these buffers here. These make a noticeable difference when tuned correctly.
Adjust client MTUs to match the OpenVPN server
You can use the following command to grep connection logs for ‘MTU’ mismatches. Use the warnings about size mismatch to adjust tun-mtu if necessary. My router defaults to 1500, which is also OpenVPN’s default, so there is no need to mess with it. Also, see warnings about adjusting tun-mtu and be sure to read about mssfix.
sudo cat /path/to/openvpn.log | grep WARNING
Which will display any warning like this:
WARNING: 'link-mtu' is used inconsistently, local='link-mtu 1500', remote='link-mtu 3000'
Set the transmit queue length
Set the TX queue length on the TUN/TAP interface. This defaults to the system OS, which in my case is 1000.
txqueuelen 2000
Default ovpn.com config (before)
client dev tun remote-cert-tls server cipher aes-256-cbc pull nobind reneg-sec 0 resolv-retry infinite verb 3 persist-key persist-tun remote-random proto udp mute-replay-warnings comp-lzo route-delay 10
My improved OpenVPN performance config file. (After)
client dev tun remote-cert-tls server compress proto udp cipher aes-128-cbc ncp-disable fast-io sndbuf 512000 rcvbuf 512000 txqueuelen 2000 pull nobind reneg-sec 0 resolv-retry infinite verb 3 persist-key persist-tun remote-random mute-replay-warnings route-delay 10
OpenVPN Performance – Conclusion
Often, even more so in work environments than at home, we are obliged to use technology, devices, software, and other tools we wouldn’t typically support. In these cases, we are still tasked with making things work, finding a workaround, and patching things up. Using OpenVPN on an Edgerouter feels a lot like that right now.
My next article should be the top five home and small business routers; what do you think? I would still include the Edgerouter 12, but I do have at least three others off the top of my head that I’m looking at next. For one, I’m interested in the Firewalla Gold, but at 2x the cost of the ER-12, it probably won’t make the list. Let’s discuss this later, yea? Please send me some suggestions to look into as well.
from https://linuxblog.io/improving-openvpn-performance-and-throughput/
--------------------------------
相关帖子:
https://briteming.blogspot.com/2017/08/openvpncipher.html
No comments:
Post a Comment